May 01, 2025
Blog PostComparing Semantic MediaWiki, Cargo, and Wikibase

What is Semantic MediaWiki?

Semantic MediaWiki is a free, open-source extension to the MediaWiki software that allows users to add structured data to wiki pages. This structured data can then be used to create dynamic lists and queries, and to automatically generate reports and other information based on the data. Semantic MediaWiki is commonly used in applications such as knowledge management systems, corporate intranets, and collaborative platforms. It is a powerful tool for organizing and querying large amounts of information in a flexible and user-friendly way.
What is Cargo?

Cargo is a MediaWiki extension that allows users to store and query structured data within a MediaWiki site. It provides a way for users to create and manage custom data tables, and to query and display that data in a variety of formats, including charts and graphs. This can be useful for organizing and presenting information that doesn't fit well within the traditional wiki page format.
What is Wikibase?
Wikibase is a software platform that powers Wikidata, a free and open knowledge base that can be read and edited by both humans and machines. Wikibase is designed to store and organize data in a structured way, and to make it easy for people to access and use this data. Wikidata is built on top of Wikibase, and provides a public database of facts and information that is freely available to everyone.
Comparing Semantic MediaWiki, Cargo, and Wikibase
Semantic MediaWiki, Cargo, and Wikibase are all tools that can be used to add structured data to a MediaWiki-powered website. Each of these tools has its own unique benefits and drawbacks, and choosing the right one for your needs will depend on the specific requirements of your project.
Semantic MediaWiki is a popular extension for MediaWiki that allows users to add structured data to the pages on a MediaWiki-powered website. This structured data can then be queried and displayed using the Semantic MediaWiki query language. One of the main benefits of Semantic MediaWiki is that it is relatively easy to use, and does not require any programming knowledge. Additionally, it is open-source and free to use.
However, Semantic MediaWiki does have some drawbacks. It can be difficult to manage large amounts of data, and it may not be suitable for very large or complex data sets. Additionally, the query language can be difficult to learn and use, which can make it challenging for users who are not familiar with it.
Cargo is another tool that can be used to add structured data to a MediaWiki-powered website. It is a more powerful and flexible tool than Semantic MediaWiki, and is designed to handle large amounts of data. Unlike Semantic MediaWiki, which uses a query language to access and display data, Cargo allows users to directly access and manipulate data using SQL. This makes it easier for users who are familiar with SQL to work with the data, and it also allows for more complex data manipulation and querying.
Wikibase is a tool that is similar to Cargo in many ways. It is a powerful and flexible tool that is designed to handle large amounts of data, and it allows users to directly access and manipulate data using SQL.
However, Wikibase has some additional features that make it more powerful and flexible than Cargo. For example, it supports the creation of multiple databases within a single installation, which can be useful for managing complex data sets. Additionally, it has built-in support for the Linked Data standard, which allows data to be easily linked and queried across different databases.
Overall, each of these tools has its own unique benefits and drawbacks, and the right choice for your project will depend on your specific requirements. Semantic MediaWiki is a good choice for smaller, simpler projects that do not require a lot of technical knowledge. Cargo and Wikibase are better suited for larger, more complex projects, and are better suited for users who are familiar with SQL.
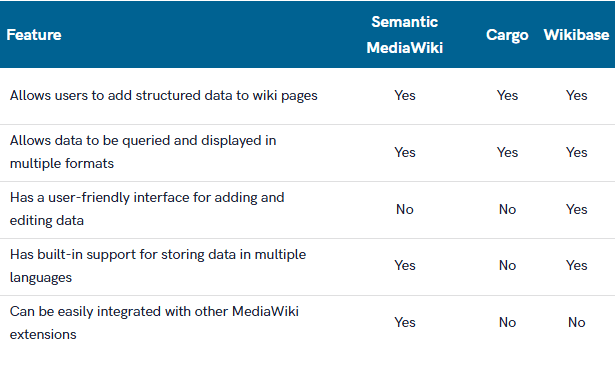
Features
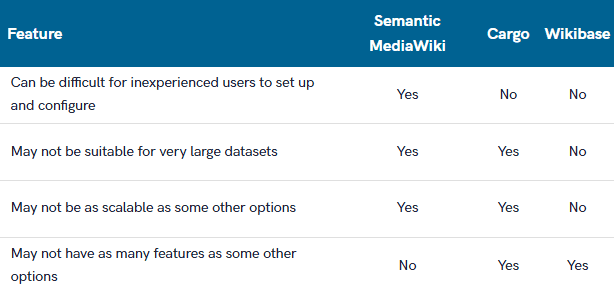
Cons
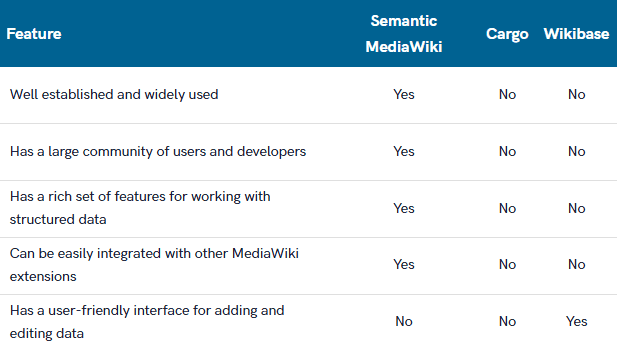
Pros
Semantic MediaWiki
Semantic MediaWiki (SMW) is the most common solution for managing structured data within MediaWiki. It is well-suited for general-purpose use cases where data needs to be stored, queried, and visualized directly within the wiki environment.
Best for:
- Wikis that require complex data relationships, inline queries, and rich visualizations such as maps, graphs, or calendars.
- Scenarios where users need to generate dynamic reports and export data in various formats.
Advantages:
- Offers a wide range of querying and visualization tools.
- Supports detailed, semantic relationships between pages.
- Integrates well with form-based data entry systems like Page Forms.
Considerations:
- Installation and configuration can be complex.
- Some features may be more advanced than necessary for smaller projects.
Cargo
Cargo is a lightweight alternative that is ideal for projects where structured data is stored primarily in templates, such as infoboxes. It uses SQL-style querying and is simpler to set up and maintain than SMW.
Best for:
- Wikis that need basic reporting and data handling using familiar SQL syntax.
- Projects with well-defined data stored in templates.
Advantages:
- Easy to install and maintain.
- Efficient for storing and querying tabular data.
- Enables SQL-style queries both inside the wiki and externally.
Considerations:
- Fewer visualization options and a smaller ecosystem.
- Less flexible when handling complex data relationships or ontologies.
Wikibase
Wikibase is designed for creating structured, multilingual knowledge graphs rather than page-centric content. It is commonly used for projects that require detailed metadata, versioning, and external data sharing.
Best for:
- Projects aiming to create or mirror knowledge bases like Wikidata.
- Use cases that require advanced data modeling, external access, or data federation.
Advantages:
- Supports multilingual labels, references, and qualifiers.
- Built for SPARQL queries and external reuse.
- Ideal for managing data as a standalone resource rather than embedding it within wiki pages.
Considerations:
- More complex to set up and manage.
- Lacks built-in support for inline queries and visualization within standard wiki pages.
- Better suited to entity-based workflows than traditional wiki editing.
Conclusion
Choosing the right tool for managing structured data in MediaWiki depends on your specific project goals and data complexity.
Semantic MediaWiki is a powerful option for wikis that require in-page queries, semantic relationships, and a wide variety of data visualizations. It’s well-suited for internal knowledge bases where users need to generate dynamic reports and explore connected information.
Cargo, on the other hand, offers a simpler, SQL-style approach that works best for data stored in templates. It’s a practical choice for smaller projects or teams comfortable with SQL who want lightweight reporting without the overhead of a full semantic layer.
For more advanced use cases, particularly those involving complex data models, external data sharing, or multilingual content, Wikibase is the preferred solution. It allows you to build structured knowledge bases similar to Wikidata, making it ideal for data reuse and integration across platforms.
If you're unsure which approach fits your needs, don’t hesitate to schedule a free, no-obligation call with us. We’re happy to help with any of your MediaWiki, Semantic MediaWiki, Cargo, or Wikibase questions.
This article is a re-written and enhanced version of our previous Semantic MediaWiki, Cargo, and Wikibase comparison.
This article is a re-written and enhanced version of our previous Semantic MediaWiki, Cargo, and Wikibase comparison.